An open, ontology-driven interoperability framework enabling secure, semantic-centric data exchange across the energy ecosystem and beyond.
About SEF
Reaching global energy sustainability goals requires seamless, secure, and flexible data exchange. Today, that interoperability is hindered by closed platforms, incompatible protocols, and vendor lock-in. The LF Energy Semantic Energy Framework (SEF) addresses these challenges by providing a distributed, open-source, multi-domain interoperability framework designed to enable semantic data representation, discovery, and reasoning across diverse systems.
LFE-SEF builds on the Semantic Interoperability Framework (SIF) developed under the EU Horizon 2020 InterConnect Project (2019–2024), which brought together 50 partners to demonstrate semantic interoperability across smart home, smart building, grid, and IoT domains. The InterConnect SIF delivered the foundational tools, methods, and specifications needed to interconnect semantically enabled services into interoperable ecosystems—capabilities that now serve as the basis for LFE-SEF.
The framework allows stakeholders to securely exchange heterogeneous data without requiring a centralized platform or disruption to existing systems. Through service adapters, semantic brokerage, reasoning capabilities, and a configurable service catalog, LFE-SEF enables trusted cross-domain information exchange. While rooted in the energy sector, its ontology-agnostic, domain-neutral design supports adoption in adjacent industries such as healthcare, agriculture, and other data-intensive domains.
Key Features
Interoperability Without a Central Platform
Interoperability originates at the stakeholder level, supported by service adapters that respect existing interfaces and workflows.
Ontology-Agnostic Architecture
While SAREF and its extensions serve as the default ontology, the framework supports any ontology expressed in RDF/OWL.
Security and Privacy by Design
All communication interfaces are secured, with integrators able to enforce their own best practices and control knowledge flows.
Flexible Deployment
Components can run across devices, edge nodes, enterprise systems, and cloud environments.
Federated Knowledge Spaces
Distributed reasoning enables semantically interoperable ecosystems that support complex queries and form the foundation for inter-domain data spaces.
Core Components
Semantic Interoperability Layer (Knowledge Engine)
Provides semantic translation and discovery capabilities using ontology-driven knowledge models. Supports any ontology expressed in RDF/OWL.
Service Store
A web-based catalog of interoperable services that enables stakeholders to register, discover, and validate services. It functions as the identity provider of the ecosystem and offers a Knowledge Explorer to visualize semantic relationships. Integrators may deploy their own instance as needed.
Service Adapters
The combination of Service Specific Adapters (SSA) and the Generic Adapter (GA) creates a unified gateway between legacy interfaces and the LFE-SEF framework, ensuring secure, trusted communication and consistent semantic mapping.
Project Roadmap
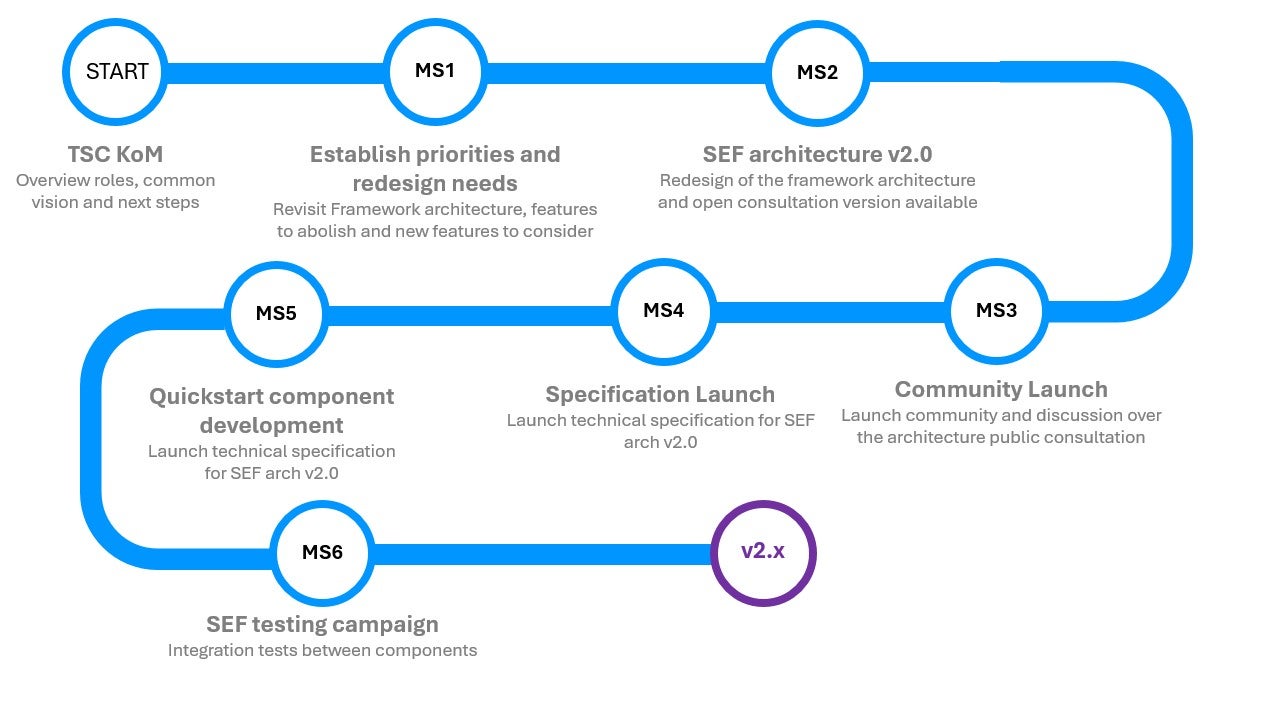
Contributing Organizations
 |  |  |
|---|
SEF Videos
Upcoming Meetings
View the calendar of all LF Energy events
Project Special Interest Group: Data Standards and Tooling
Project Lifecycle Stage: Sandbox

Sponsored Session: Collaborative Analytics and Semantic Inter... José Ricardo Andrade & Fábio Coelho
September 22, 2025 2:40 pm